Periodic
Classification of Elements || Class 10th Science || CBSE Notes || Study World
Dear Students, Today we are providing notes of Class 10th Chapter-
Periodic Classification of Elements Notes. These notes are very helpful for the
students of 10th Class to scored good marks.
This Chapter Includes the following topics
• Introduction Classification of
elements
Periodic classification of Element
Classification
of elements:
It is the systematic
arrangement of element in such a way that the element with similar properties
are placed together while the elements with dissimilar properties are separated.
Need
for classification of elements
Since there are 118 element known at present and
it is not an easy task to study each and every element and their property
individually.
So, in order to systematize the study of
chemistry and to make it more comprehensive, it is necessary to classify the
element.
Earlier attempt made in the classification of
element:
Dobereiner’s Law of Triads
This law as given by a German Chemist J W
Dobereiner in 1871, which state that, when a group of three element with
similar properties are arranged in the order of their increasing atomic mass
than atomic mass of the middle element is found to be the arithmetic mean of
the atomic mass of the other two elements.
Example:
(1)
Element
|
Li
|
Na
|
K
|
Atomic
Mass
|
7
|
23
|
39
|
Atomic Mass of Na = ( 7 + 39) ÷ 2 = 46 ÷ 2 = 23
(2)
Element
|
Ca
|
Sr
|
Ba
|
Atomic
Mass
|
40
|
88
|
137
|
Atomic Mass of Sr = ( 40 + 137) ÷ 2 = 177 ÷ 2 =
88.5 ≅ 88
(3)
Element
|
Cl
|
Br
|
I
|
Atomic
Mass
|
35•5
|
80
|
127
|
Atomic Mass of Na = ( 35•5 + 127) ÷ 2 = 162.5 ÷
2 = 81.25 ≅ 80
Limitation
of Dobereiner’s Triad:
Dobereiner could identify only three triad as it
was not possible to arrange all the then known element according to this law.
Hence this law reject later on.
Newland’s
Law of Octave:-
This law was given by an English chemist John
Alexander Rina Newland
In 1866, which states that when the elements are
arranged in the order of their increasing atomic mass then the properties of
every 8 elements starting from a given element is the repetition of the first
like the 8th note in an octave of music.
Li Br B C N O F
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl
K Ca
Limitations
of Newland’s Law of Octaves:
(1) This law is applicable only upto calcium.
(2) This law worked only with the lighter
elements.
(3) Newland assumed that onle 56 elements
existed in nature and no more element would be discovered in future.
(4) Newland in some cases put two elements in
the same slot.
Example: Cobalt (Co) Nickel (N)
Mendeleev
Classification of Elements
In 1869, a Russian Chemistry teacher
Dimitri Ivanovich Mendeleev slightly
modified Newland’s octave and arranged
the then known 63 elements in the order of their increasing atomic mass and
found out that the property of the elements appear at regular interval. This repetition
in properties of the elements is called Mendeleev’s periodic law and from the
table of elements and called Mendeleev’s
periodic table.
Modern
Periodic Law:
The properties of the element are the periodic
function of their increasing atomic masses i.e. When the element are arranged
in order of increasing atomic masses then their properties appear at regular
intervals.
Mendeleev’s
Periodic Table:
It is the systematic arrangement of element in
certain group and periods when the elements are arranged in order of their increasing
atomic mass.
Characteristics
of Mandeleev’s Periodic Table :
(1) There are 8 vertical column in Mendeleev’s
periodic table called groups.
(2) The properties of elements in a group of
similar.
(3) There are six horizontal rows in the
Mendeleev’s periodic table called period.
(4) The property of element in the periodic is
different.
(5) There are a few groups in original Mendeleev
periodic table.
Gaps
in Mendeleev Periodic Table
While farming his table he left some gaps in his
table for those elements which were to be discovered
Mendeleev thought that these elements would be
discovered later on and even predicted their properties from their position in
the periodic table.
Elements which were discovered later on were Gallium,
Scandium (Sc) Germanium (Ge)
Advantages
and merits of Mendeleev periodic table:
(1) It made the study of chemistry more
systematic and comprehensive.
(2) It give better classification that other as
it is based on the more fundamental properties called atomic mass.
(3) It predicted the existence of some elements
that has not been discovered at that time.
(4) It could accumulate noble gas when they
would be discovered.
Anomalies/
Drawbacks/ Shortcoming/ Limitations/ demerits or disadvantages of Mendeleev
periodic table:
1. Position
of Isotopes: The position of isotope
could not be explained as we know that the isotopes are the items of the same
elements having same atomic number, but different atomic mass. So, they could
have got separated place in the periodic table; but the isotopes are placed at
the same place in the Mendeleev’s periodic table.
2. Wrong order of atomic mass of the same
elements could not be explained.
3. A correct position could not be assigned to
the hydrogen in the periodic table.
4. As some place chemically similar element are
separated and dissimilar elements are grouped together.
Modern
Classification of Elements:
Limitation in the periodic table of Mendeleev
led to the conclusion that the atomic mass could not be the basis of
classification of elements but atomic number could be.
So in 1913, Henry Moseley slightly modified
Mandeleev classification by arranging the elements in the order of their
increasing atomic number and found that properties of the elements appear at
regular intervals.
Modern
Periodic Law
The properties of the elements are a periodic
function of their increasing atomic number, i.e. when elements are arranged in
the order of increasing atomic number then the properties appear at regular
intervals.
Modern
Periodic Table
It is the systematic
arrangement of elements in certain groups and periods when the element are
arranged in the order of their increasing atomic number.
Characteristics
of Modern Periodic Table
(1) It consists of 18 verticle columns called
groups.
(2) The properties of all the elements in a
group are similar.
(3) All the elements in same group have same
number of valence electrons and have same valency.
(4) The valency electron of the elements
determine their group number.
(5) The elements on the extreme right of the
periodic table are called noble gas.
(6) Elements in group 3-12 are called transition
element.
(7) There are two separate rows in at the bottom
of the periodic table called lanthanides and actinides.
(8) There are seven horizontal rows in modern
periodic table called periods.
(9) The properties of all the elements are
different.
(10) Each period bring with alkyl metals except
first which start from hydrogen and at and at noble gases.
(11) The number of shell in the electronic
configuration of the element determine its product number.
(12) In the periodic table, metal have been
separated from non-metals by some element called metalloids which are place
diagonally regularly in the periodic
table
Isotopes :
Isotope of the atom of same elements having same
atomic number but different atomic mass.
Example:
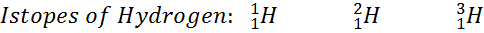



Isobars: Isobars are the atom of different elements having
different atomic number but same atomic mass.
Example:
Isotones :
Isotones are the atoms of different element
having same number of neutrons.
Example:
Lanthanides and Actinide:
The 14 rare earth element having similar
properties which being after Lanthanium
are called Lanthanides and those starting from Actinium are
called Actinide.
Lanthanides 58 to 71
Actinide 90 to
103
Halogens
The element fluorine (f) chlorine (Cl) bromine (Br) Iodine ( I ) Astatine (At)
placed in group 17 modern periodic table are called halogen as they form salt
with alkyl metals.
Merits of Modern Periodic Table:
(1) The modern periodic table is based on the
atomic number of elements, which is the most fundamental property of element.
(2) The modern periodic table help us to
understand why Elements in a group show similar properties but elements in
different group show different properties.
(3) The modern periodic table explain the reason
for the periodicity in properties of element.
(4) The modern periodic table tell us why the
properties of elements are repeated after 2, 8, 18, 32 element.
(5) There is no anomalies in the arrangement of
element in the modern periodic table .
(6) It has made the study of chemistry systematic
and easy it act as an air of memory.
(7) A periodic table chart is used as a teaching
aid in the chemistry in school and colleges.
(8) The type of compound found in by an element
can be predicted by knowing its position in the periodic table.
Characteristics of Period
The horizontal rows in the modern periodic table
are called period.There are seven periods in Modern Periodic Table number 1 to 7.
Valency Electrons (or outermost electron )
On moving from left to right in a period, the
number of valence electron in element increase from 1 to 8.
Valency
On moving from left to right in each short
period, the valency of elements increases from 1 to 4 and then
decreased to 0
Size of Atom: On moving from left
to right in a period of the periodic table the size of atom decrease.
Metallic Character: On moving from left to right in a period, the metallic
character of elements decrease but the non metallic character increases.
Chemical Reactivity: On moving from left to right in a period, the chemical
reactivity of element first decrease and then increases.
Nature of Oxide: On moving from left to right in a period, the basic nature
of the oxidedecreases and the acidic nature of oxide increases.
Characteristics of Group
Valency Electron : All the electrons of a group of periodic table have the
same number of valence electrons.
Valency: All the elements in a group have the same valency.
Size of Atom: On going down in a group of periodic table, the size of
atom increase .
Metallic Character: On going down in a group of the periodic table, the
metallic character of the element increase.
Chemical Reactivity: The chemical reactivity of the metal increase on going
down in a group of periodic table.
Nature of oxides: On going down in a group of periodic table, there is no
change in the nature of oxide of element .
Some Important Definitions:
Ionisation: It is the maximum energy required to remove an electron
from the outermost shell of an element.
Electro positivity: It is the tendency of element to lose electron or to gain
positive charge it increases with the increase in atomic size. Metal are
electropositive element electron.



Comments
Post a Comment