Metal and Non-Metal || Class 10 || Science || CBSE Notes
Dear Students, Today we are going to share the Notes of Carbon and its Compound. These notes are prepared by the experienced teachers. These notes are free to all the students. These notes has been prepared according to the CCE pattern of school education based on NCERT Syllabus prescribed by the Central Board of School Education for Class X. All the important topics are covered in these notes.
There are 115 chemical elements known as present. On the basis of their properties, all the element can be divided into two main group: Metal and Non-Metal.
Metals: Metals
are the element that conduct heat and electricity and are malleable and ductile.
†All
metals are solid expect Mercury.
†
Metals are the element except hydrogen which form positive Ion by loosing
electron.
†
Metal are electropositive
†
The most abundant metal in the earth crust is aluminium.
Physical
property of matter
(1)
Metal are malleable that is metal can be beaten into thin sheet with a hammer
without breaking it .
(2)
Metal are ductile that is metal can be drawn into wire.
(3)
Metal are good conductor of heat and electricity .
(4)
Metal are lustrous and Shiny and can be polished.
(5)
Metal are generally hard except Sodium and potassium which are soft and can be
cut with a knife.
(6)
Metal are strong except Sodium and potassium.
(7)
Metal are solid at room temperature.
(8)
Metal have high melting point and boiling point except Sodium and potassium
which have low melting and boiling point.
(9)
Metal have high density except Sodium and potassium which have low density.
(10)
Metal are sonorous that is metal makes sound when it hit with an object.
(11)
Metal usually has Silver or grey colour except Copper and gold.
Chemical property of
Metal
The
most important chemical property of matter are as follow:
(1).
Reaction of metal with oxygen :-When metal are burnt in air, airn they react
with oxygen of air to form metal oxide.
Metal + Oxygen ª
Metal oxide
(c)
Aluminium metal burn in air to form Aluminium oxide
4 Al + 3O2 ª
2Al2 O3
The
aluminium oxide show acidic as well as basic property therefore known as amphoteric oxides. Zinc also form amphoteric oxides.
Amphoteric
oxides reacts with acid and base to form salts and water.
Reaction of Metal with
Water:
When metals react with water (cold or hot) the product formed are metal Hydroxide or hydrogen gas.
When metals react with water (cold or hot) the product formed are metal Hydroxide or hydrogen gas.
Metal
+ Steam ª
Metal Oxides + Hydrogen
Metal
Oxides + Water ª
Metal Hydroxide
Example :
(i)
Potassium reacts violently with cold water to form potassium hydroxide and
hydrogen.
(ii)
Aluminium reacts with steam to form Aluminium oxide and hydrogen gas.
(iii)
Reaction of metal with acids : - Metals usually
displace hydrogen from dilute acids. Only less reactive metal like
Copper, silver and gold do not displace it.
Metal
+ dilute acid ª
Metal Salt + Hydrogen
Example:-
Sodium metal reacts with hydrochloric acid to form sodium chloride and hydrogen.
Some
metal like Copper does not react with HCl.
Reaction of metals with
salt solution:
When
a more reactive metal is put in the salt solution of less reactive metal, then
the more reactive metal displace the less reactive metal from its salt solution.
i.e.
Salt
solution of Metal B + Metal A ª
Salt solution of Metal A + Metal B.
Example:
The reaction of Zinc with copper sulphate.
Reaction
of Metal with Chlorine:
Metal
react with chlorine to form metal chlorides.
Reaction of Metal with
Hydrogen :
Most
of the metals do not combine with hydrogen. Only a few metal like Sodium, Potassium,
calcium and magnesium react with
hydrogen to form hydrides.
It is a freshly prepared mixture of one
part of concentrated nitric acid and 3 part of concentrated hydrochloric acid
is highly corrosive and blooming liquid which can dissolve all the metal even
gold and potassium too.
Non-Metals
Non-Metal
are the element that do not conduct electricity and neither malleable nor
ductile.
†
Out of 20 non-metal, 10 non-metal are solid, one non-metal is bromine is liquid, whereby
remaining 11 are gases.
†
Non-Metals are the element which form negative ion by gaining electrons.
† Non-Metals are electronegative.
† Hydrogen only non metal which loses electron
Physical property of Non-Metal
(1)
The physical property of Non-Metal are just the opposite of Metals:
(2)
Non-metals are neither malleable nor ductile. non metal are brittle
(3) Non-metals do not conduct heat and
electricity except graphite.
(4)
Non-metals are non lustrous (not shiny).
They are dull.
(5)
Non-metals Generally softexcept diamond which is extremely hard non metal
(6)
Non-metals are not strong. there are easily broken
(7)
Non-metals may be solid liquid or gas at room temperature
(8)
Non-metal have comparatively the low melting and boiling point except Diamond whose
melting point is about 3500° C
(9)
Non-metal have low density. i.e. they are light substance .
(10)
Non-Metal are non-sonorous. They do not produce any loud sound when hit with an
object.
(11)
Non-metal are of many colour.
Some exception in Physical
Property of Non-metal and Metal
(1)
Carbon is in the form of graphite conduct electricity is a non-metal.
(2)
Iodine is a non metal which is lustrous.
(3)
Carbon is the form of diamond (Non-metal) is extremely hard
(4)
Mercury metal is liquid at room temperature.
(5) Sodium, Potassium, Cesium and gallium
metal are low melting point whereas diamond is a non-metal and have a high
melting and boiling point.
(6)
Alkali metals have low density like Sodium and Potassium.
Chemical Properties of
Non-Metal
The
important chemical properties of non-metal are given below:
(1) Reaction of
non-metal with oxygen: Non-metal react with
oxygen to form acidic oxides or neutral oxides. The acidic oxides of non-metal
dissolve in water to form acids.
Example:
(a)
Carbon burns in air, it reacts with oxygen of air to form acidic oxides called
carbon dioxide.
The acidic oxides carbon dioxide dissolved in water to form an acid called carbonic acid.
The acidic oxides carbon dioxide dissolved in water to form an acid called carbonic acid.
(2) Reactions of
Non-Metal with Water: Non-metal do not reacts
with water or steam and hence do not evolve hydrogen gas.
(3) Reaction of
Non-metal with Dilute acid: Non Metal do not react
with dilute acids.
(4) Reaction of
non-metal with Salt Solution: A more reactive
non-metal displaced a less reactive non-metal from its salt solution
Example
(5) Reaction of Non-metal with Chlorine:- Non-metal react with chlorine to form covalent chloride which are non-electrolytes (and do not conduct electricity)
(5) Reaction of Non-metal with Chlorine:- Non-metal react with chlorine to form covalent chloride which are non-electrolytes (and do not conduct electricity)
Example
(6) Reaction of Non-metal with Hydrogen :- Non metal react with Hydrogento form covalent hydrides.Non metals form covalent hydrides because non-metal atoms cannot give electron to hydrogen atom to form hydride ions.
(6) Reaction of Non-metal with Hydrogen :- Non metal react with Hydrogento form covalent hydrides.Non metals form covalent hydrides because non-metal atoms cannot give electron to hydrogen atom to form hydride ions.
Metal
are used of a large number of purpose. Some of the uses of a metal are given below:-
(1)
Copper and Aluminium metal are used to make wires to carry electric current
because of its low electric resistance and has very good conductor of
electricity.
(2)
Iron Copper and Aluminium metal are used to make household utensil and factory equipment.
(3)
Iron is a used as a catalyst in the preparation of ammonia gas by Haber’s process.
(4)
The aluminium foils are used in packing of medicine a cigarette and food
material
(5)
Chromium and Nickel metal are used for electroplating
(6)
Zinc is used for galvanisation iron to protect it from rusting
(7)
Silver and gold metal are used to make Jewellery
(8)
Gold foil are used to make decorative
sweets.
(9)
The liquid metal mercury is used to make thermometer.
(10)
Sodium, Titanium, zirconium metals are used in atomic energy (nuclear energy) and
space science project.
(11)
Zirconium metal is used in making bullet proof alloy steel.
Uses of Non-metal
The important uses of non-metal are as follow:
(1) Hydrogen is used in the
hydrogenation of vegetable oil to make vegetable ghee ( or vanaspati ghee)
(2) Hydrogen is used in the manufacture
of ammonia.
(3) Liquid hydrogen is used as a rocket
fuel.
(4) Carbon in the form of graphite is
used for making electrode of electrolyte cell and dry cell.
(5) Nitrogen is used in the manufacture
of ammonia, nitric acid and fertilizer.
(6) Due to its inertness, nitrogen is
used to preserve food materials.
(7) Compound of Nitrogen like Tri Nitro
Tolune and nitro glycerin used as explosive.
(8) Sulphur is used for manufacture of
sulphuric acid.
(9) Sulphur is also called as a
fungicide and in make making gun powder.
(10) Sulphur is also used in the
vulcanization of rubber.
How do metal and non-metal
react?
When
metals react with non metal they form ionic
compound. On the other hand, when non metal react with other non metals
they form covalent compound.
The
force which links the atoms in a molecule is called a chemical bond.
Electronic
configuration of Noble gases:
Element
|
Symbol
|
Atomic Number
|
Electronic Configuration
|
Helium
|
He
|
2
|
2
|
Neon
|
Ne
|
10
|
2, 8
|
Argon
|
Ar
|
18
|
2,
8, 8
|
Krypton
|
Kr
|
36
|
2, 8, 18, 8
|
Xenon
|
Xe
|
54
|
2,
8, 18, 18, 8
|
Radon
|
Rn
|
86
|
2, 8, 18, 32,
8
|
To
have 8 electrons in the outermost shell is known as Octet of the electrons. Most of the inert gases have octet of
electrons in their valence shells. Only in case of helium the number of
outermost electron is 2.
Chemical
bond: It is a force which binds the participating atom together in a molecule.
Cause of Chemical Bond:
Everything
in the world wants to attain minimum energy state, that is to become more and
more stable. For atom this stability comes only if there octet is completed
that is their electronic configuration is similar to noble gas.
To
attain noble gas configuration atoms of various elements react with each other
to form a chemical bond.
How an atom can achieve
noble gas configuration:
E
By losing electrons in the atom of an element.
E
By gaining electrons from the atom of other element.
E
By the mutual sharing of electrons.
Ions
An
iron is an electrically charged atom (or a group of atoms). Example of ions are : Sodium ion, Na+
, Magnesium ion Mg2+ , Chloride ion (Cl)‾ and oxide ion O2 ─
An
ion is found by the loos or gain of electron by an atom. So, it contain an
equal number of electron and protons. Ions are of two type: Cations and Anions
1. Cations:-
A positively charged ion is known as cations. A cation is formed by loss of one
or more electrons by an atom. For example: Sodium atom loses 1 electron to form
a sodium ion Na+, which is a
cation:
2. Anion:-
A negative charged ion is known as anion. An anion is formed by gain of one or
more electron by an atom. For example, of chlorine atom gain 1 electron to form
a chloride ion (Cl)‾ which is an anion.
Formation of Positive ions
(or cations): The atom loses electrons to form
possible charge and cations.
For
example:
Formation of Negative
Ion or (Anions) : The non-metal atoms
accept electrons to form negative ions or anions.
(1)
Ionic bond
(2)
Covalent bond
Ionic Bond:
The chemical bond formed by the transfer of electrons from one and another is
known as ionic bond.
+-The loss and gain of electrons takes place in such a way that both the participating atoms can achieve noble gas configuration.
For
example:
Ionic
Compound / Electrovalent Compound
These
are the compound which contain electrovalent or ionic bond i.e. they are formed
by the complete transfer of electrons from the atom of an element to the atom
of another elements.
e.g. Copper Sulphate (CuSo4), Ammonium Chloride (NH4Cl) Calcium
Nitrate (Ca(Na3)2) , ferrous sulphate (FeSO4)
, ferric chloride (FeCl3), Lead
sulphate (PbSO4) , mercuric oxide (HgO).
Covalent
Bond
It is the chemical bond by the mutual sharing of
electrons between the participating atoms of non-metal.
The sharing of
electron takes place in such a way that each atom in the resulting molecules
attains noble gas configuration.
Example:
Types of Covalent bond:
(1)
Single Covalent Bond
(2)
Double Covalent Bond
(3)
Triple Covalent Bond
Single Covalent Bond:
It
is formed by sharing of one pair of
electron and is represented by (―).
Double Covalent Bond
It
is formed by the sharing of two pairs of electrons and is represented by (=) .
For example:
It
is formed by the sharing of three pair of electrons and is represented by (º).
Example:
Covalent Compound
These
are the compound which contain covalent bond that is they are formed by the
mutual sharing of electrons between the participating atoms of non-metals.
For example:
Surcose
(C12H22O11), Glucose (C6H12O6),
Ethanol (C2H5OH), Methanol (CH3OH), Methane
(CH4) etc.
Difference between
Ionic and Covalent Compounds
Ionic or Electrovalent Compounds
|
Covalent Compound
|
|
1
|
They
contain electrovalent or ionic bond i.e. they are formed by the complete
transfer of electrins from the atom of one element to the atom of other
element.
|
They
contain covalent bond i.e. they are formed by the mutual sharing of electrons
between the participating atoms of non-metal.
|
2
|
Example: NaCl,
CuSo4, KCl, MgCl2 , AlCl3 , CaCl2 , MgO,
CaO, etc.
|
Example: C12H22O11
, C6H12O6 , C2H5OH, CH3OH, CH4 etc.
|
3
|
They
usually exist as crystalline solid.
|
They
may be solid, liquid or gases
|
4
|
They are good
conductor of electricity.
|
They are poor
conductor of electricity.
|
5
|
They
are usually soluble in water.
|
They
are usually insoluble in water.
|
6
|
They are
insoluble in organic solvents like Alcohol, Benzone, Ether, Petrol, etc.
|
They are
soluble in organic solvents like Alcohol, Benzone, Ether, Petrol, etc.
|
7
|
They
have high melting and boiling point
|
They
have low melting and boiling point
|
Occurrence of Metal
The
earth crust is the major sources of metals. Sea-Water also contains salts of
metals like Sodium Chloride, magnesium chloride etc.
Most
of the metals are quite reactive and hence do not occur as free elements in
nature.
Only
a few less reactive metals like Copper, silver, gold and platinum are found in
free state.
Copper
and silver metal occur in free state as well in combined state in the form of
compound.
All
the metal which are placed above copper in the reactivity series are found in
nature only in the form of their compound.
Minerals:-
It
is a naturally occurring organic or inorganic substance which is mined from the
earth e.g. Coal, Petroleum, natural gas, Diamond, rock salt (NaCl)
Ore:
It is the mineral from which the metal can be extracted profitably. All the ores
are mineral but all the mineral are not ores. E.g. Na from NaCl, Al from Aluminium
oxide Al2O32H2O, Zn from Zinc Carbonate ZnCO3
and Iron (Fe) from Iron oxide (Fe3O3).
Gangue/Matrix: These
are the unwanted importance such as sand, rocky materials, earthy particles present
in the Mineral ore.
Flux :
It is a substance which combines with the gangue to form a lighter, fusible
material called slag.
Flux + Gangue ª
Slag
Slag:
It is lighter fusible material formed by the action of flux and gangue.
Flux + Gangue ª
Slag
Metallurgy:
It is a special branch of chemistry which is deals with the study of various steps
that are involved in the extraction of metal from its naturally occurring ore
followed by the refining of metals.
Anode: It
is an electrode where the oxidation i.e. the loss of electrons takes place.
Cathode:
It is an electrode where the reduction i.e. the gaining of electrons takes
place.
Electrolysis:
It is the process of decomposition of electrolyte by the passage of
electricity.
Extraction of Metals
To
obtain metal from its ore is called extraction of metals. The ore are converted
into free metals by the number of steps which depends upon the type of ore used,
nature of the impurities present and reactivity of the metal to be extracted.
The
three major steps involved in the extraction of metal from its ore are:-
(1)
Concentration of Ore ( or Enrichment of ore)
(2)
Conversion of concentrated ore into metal, and
(3)
Refining (Purification) of impure metal.
(1) Concentration of
ore (or Enrichment of Ore): Ore is an impure
compound of a metal containing a large amount of sand and rocky material. Before
extracting the metal from an ore, it is necessary to remove these impurities
(or gangue).
The
method used for removing gangue from ore depends on some difference in the
physical properties or chemical properties of the ore or gangue. Concentration
of ore is also known as enrichment of ore.
Conversion of Concentrated
Ore into Metal:
For
this we group the (element) metal into the following three categories:-
(1)
Metal of high reactivity
(2)
Metal of medium reactivity
(3)
Metals of low reactivity
Extraction of Highly
Reactive Metals:ª The
highly reactive metals such as potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium and
Aluminium are extracted by the electrolysis of their molten chlorides or oxides.
The metal extracted by the electrolysis is very pure. They do not contain any impurities.
During the electrolysis of molten salts the metals are always produce at the
cathode.
For example:
We cannot use an aqueous solution of sodium chloride to obtain Sodium metal because electrolysis of Sodium Chloride solution will provide Sodium Hydroxide but not sodium metal.
We cannot use an aqueous solution of sodium chloride to obtain Sodium metal because electrolysis of Sodium Chloride solution will provide Sodium Hydroxide but not sodium metal.
The
moderately reactive metals which are in the middle of reactivity series are
extracted by the reduction of their oxide with carbon, ammonium, sodium or
calcium.
It
is easier to obtain metals from their oxide (by reduction) than from carbonates
and sulphides.
The
concentrated ore can be converted into metal oxide by the process of calcination or roasting.
(1)
Calcination: Calcination is a
process in which a carbonate ore is heated strongly in the absence of air to
convert it into metal oxide. For example,
Zinc occurs as zinc carbonate in calamine
ore (ZnCO3). When ZnCO3 is calcined, it decomposes to form zinc
oxide and carbon dioxide.
Calcination convert zinc carbonate into zinc oxide.-
Calcination convert zinc carbonate into zinc oxide.-
(2) Roasting:
It is the process in which a sulphide ore is strongly heated in the presence of
air to convert it into metal oxide. For
example: Zinc occurs as sulphide in zinc blende ore (ZnS), When ZnS is
strongly heated in air it form zinc oxide and Sulphur dioxide.
Thus roasting converts Zinc sulphide into zinc oxide.
Thus roasting converts Zinc sulphide into zinc oxide.
F
The metal oxides obtained by calcination or roasting of ore are converted into
free metal by using reducing agents like carbon, aluminium, sodium or calcium.
(1) Reduction of Metal Oxide
with Carbon: The oxide of comparatively less reactive metals like Zinc,
Iron, Nickel, tin, lead, copper are usually reduced by carbon as a reducing agent.
For example:
Even
the less reactive metal copper is extracted by the reduction of its oxide with
carbon.
(2) Reduction of Metal
oxide with Aluminium:
Aluminium
which is more reactive metal can also be used as a reducing agent in the
extraction of metal from their oxides.
This
is because a more reactive metal like aluminium can displace a comparatively
less reactive metal from its metal oxide to give free metal.
For example:-
For example:-
The
reduction of metal oxide to form metal by using aluminium powder as a reducing
agent is also called thermite reaction.
Extraction of Less
Reactive Metal:-
The
less reactive metal which are quite low in the activity series are extracted by
reduction of their oxide by heat alone.
For example:-
Mercury metal can be extracted by heating its sulphide ore in air. Mercury metal are produced from the sulphide ore
cinnabar HgS, it consists of roasting and then heat.
(2) Extraction of Copper:-
(2) Extraction of Copper:-
The
process of purified impure metal is called refining of metals. The most impure
and widely used method for refining impure metals is electrolytic refining.
Electrolytic Refining:
Electrolytic refining meaning refining by electrolysis. Many metal like copper,
zinc, tin, lead, ch+romium, nickel, silver and gold and refining electrolytically.
For the refining of an impure metal by electrolysis:-
(a)
A block of the metal is made anode.
(b)
A thin strip of the pure metal is made cathode.
(c)
A water soluble salt of the metal to be refining defined is taken as
electrolyte.
Electrolytic refining
of Copper:
A
lump of impure carbon metal and a thin strip of copper are dipped in the
solution of copper sulphate. Impure lamp of metal is concentrated with the
positive polled and thin strip of pure matter is connected with the negative
pole.
When
electric current is passed through the solution, pure metal from anode moves
towards cathode and is deposit over it. Impurities present in the metal are
settled near the bottom of anode in the solution. Settle impurities in the
solution settled impurities in the solution are called anode mud.
At Anode :- Cu ― 2e―
ª Cu + +
At Cathode :- Cu 2 + + 2 e― ª
Cu














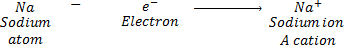



























Comments
Post a Comment