Chemical Reaction and Equations || Class 10th Science || CBSE Notes || Study World
Dear Students. Today we are providing Chemical Reaction and Equation Notes. These are helpful for the CBSE Board Examination.
Important Topic in this Chapter :
Chemical Reaction :
Chemical reactions are the processes in which new substances with new properties are formed.
Important Topic in this Chapter :
· Chemical Reaction
· Characteristics of Chemical
Reactions
¨Evolution of Gases
¨Formation of Precipitate
¨Change in Colour
¨Change in temperature
¨Change in State
· Chemical Equation
¨ Balanced Chemical Equation
¨Unbalanced Chemical Equation
· Types of Chemical Reactions
¨Combination Reaction
¨ Decomposition Reaction
¨ Displacement Reaction
¨ Double Displacement
Reaction
· Oxidation and Reduction
Reaction
¨ Oxidising agent
¨ Reducing agent
· Effect of Oxidation Reaction
in Everyday Life
· Corrosion
· Rancidity and its prevention
Chemical Reaction :
Chemical reactions are the processes in which new substances with new properties are formed.
The substances which take place in a chemical reaction are called reactants.
The new substances produced as a result of chemical reaction are called products.
The burning of magnesium in air to form magnesium oxide is an example of chemical reaction.
Characteristics of Chemical Reactions: The important characteristics of chemical reaction are as :
(1)
Evolution of gas
(2)
Formation of precipitate
(3)
Change in colour
(4)
Change in state
(5)
Change in temperature
Any
one of these general characteristics can tell us whether a chemical reaction
has taken place or not.
Example:
If on mixing two substance any gas is evolved, then we can say that a chemical
reaction has taken place.
We
will now give example to show all the characteristics of a chemical reaction
one by one
(1) Evolution of Gases:
Some chemical reaction are characterised by the evolution of gases.
Example: When
zinc granules react with dilute sulphuric acid then bubbles of hydrogen gas are
produced.
(2) Formation of Precipitate:
Some chemical reaction are characterised by
the formation of precipitate.
Example: When
potassium iodide solution is added to the solution of Lead Nitrate, then yellow
precipitate of a lead iodide is found.
(3) Change in colour: Some
chemical reaction are characterised by change in colour.
Example: When
citric acid react with potassium permanganate solution then purple colour of
potassium permanganate solution disappear
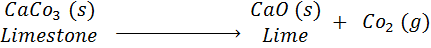
(4) Change in temperature:
Some chemical reaction are characterised by
change in temperature
Example : When
quicklime react with water then slaked lime is formed and a lot of heat produce which
change the temperature of slaked lime.
Change in State: Some
chemical reactions are characterised by change in state.
Example : When
wax is burned, then water and carbon
dioxide are formed I.e. solid state
change into liquid (water) and gases (CO2).
Chemical Equation
The
method representing a chemical reaction with the help of symbol and formula of
substance involved in it is known as chemical equation
Example: If
the chemical reaction
Zinc
+ Sulphuric acid ―> Zinc Sulphide + Hydrogen
has to be written in the symbol then it
becomes chemical equation in the form of symbol
Balanced and Unbalanced Chemical Equations:
Balanced and Unbalanced Chemical Equations:
Balanced Chemical Equation:
A balanced chemical equation has an equal
number of atoms of different elements in the reactant and product.
Unbalanced Chemical Equation:
An unbalanced chemical equation has an equal number of atom of one or more
elements in a rectant and products.
Example:


Types of Chemical Reactions: Some of the important type of chemical reaction are:
(1) Combination
Reaction
(2) Decomposition
Reaction
(3) Displacement
Reaction
(4) Double
Displacement Reaction
(5) Oxidation
and Reduction Reaction
Combination
Reactions: Those reaction in which two or more substance combine to form a
single substance, are called combination reactions.
Example:
Decomposition
Reactions: Those reactions in which a compound split up into two or more
simpler substance are known as decomposition reactions. It is just the opposite
of combination reaction.
Example:
Displacement reaction: Those reactions in which one element taken takes the place of another element in a compound are known as displacement reaction.
Double Displacement Reaction:
Those reactions in which two compound react by an exchange of ion to form two
new compounds are called double displacement reactions.
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
Oxidation:
The addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation.
The
removal of hydrogen from a substance is also called oxidation.
Reduction:
The addition of hydrogen to a substance is called as reduction.
The
removal of oxygen from substance is called reduction.
Oxidising agent:
(1) The substance which gives oxygen for oxidation is called an oxidising agent.
(1) The substance which gives oxygen for oxidation is called an oxidising agent.
(2)
The substance which removes hydrogen is called oxidising agent.
Reducing agent:
(1) The substance which gives oxygen for reduction is called reducing agent.
(2)
The substance which removes oxygen is also called a reducing agent.
The
oxidation and reduction reactions are called Redox reactions.
Effect of Oxidation Reaction in Everyday Life
There are two common factor of Oxidation reaction which we observe in daily life.
(1) Corrosion of metals
(2)
Rancidity of food.
Corrosion: Corrosion is the process in which metals are eaten up gradually by the action of air and moisture or a chemical (such as an acid) on their surface. Rusting of iron metal is the most common form of corrosion.
The
rusting of iron is redox reaction. Rusting involved unwanted oxidation of iron
metal which occur in nature on its own.
Corrosion weakens the iron and steel objects and structure such as railing, car bodies, bridge and ships etc, and short their life.
Rancidity: The condition produced by the aerial oxidation of fat and oil in foods marked by unpleasant smell and taste is called rancidity.
Rancidity
spoils the food materials prepared in fats and oil which has kept for a
considerable time and make them unfit for eating.
Rancidity can be prevented by following:
(1)
Rancidity can be prevented by adding anti-oxidants to food containing fats and
oil.
(2)
Rancidity can be prevented by packing fat and oil containing food in Nitrogen
gas.
(3)
Rancidity can be retarded by keeping food in the refrigerator.
(4)
Rancidity can be retarded by storing food in the air tight container.
(5)
Rancidity can be retarded by storing food in away from light. 














Comments
Post a Comment